tree in bud opacities treatment
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. HealthTap doctors are based in the US board certified and available by text or video.
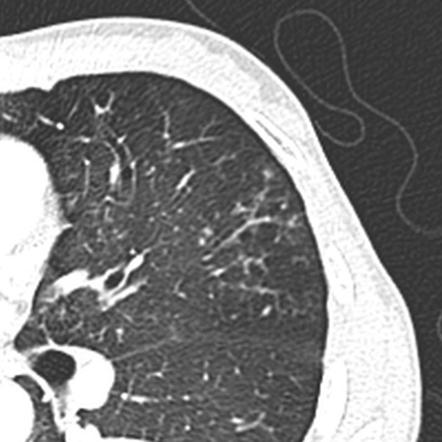
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
In the December 2009 issue of the AJR.

. Jennifer Hong BA Francisca Zuazo MD Hanyuan Shi MD 1 1 Tulane University LA New Orleans. Tree in bud opacification refers to a sign on chest CT where small centrilobular nodules and corresponding small branches simulate the appearance of the end of a branch belonging to a tree that is in bud. Thus the bronchioles resemble a branching or budding tree and are usually somewhat nodular in appearance This morphologic pattern can be seen in a wide variety of diseases as illustrated by Gosset et al.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. Is a 7mm lung nodule big. Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
Respiratory infections cause about 72 of cases with 39 due to Mycobacterial cases 27 due to other bacteria and 3 due to viruses. Malignancy can be associated with the tree-in-bud sign. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of TIB opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with TIB opacities.
Board-certified doctor 247 in less than one minute for common issues such as. Although initially described in 1993 as a thin-section chest CT finding in active tuberculosis TIB opacities are by. Diagnosis and Treatment of NTM Lung Infections Anne E.
TREE-IN-BUD OPACITIES LEADING TO A DIAGNOSIS OF SARCOID Abstracts. TIB opacities represent a normally invisible branches of the bronchiole tree 1 mm in diameter that are severely impacted with mucous pus or fluid with resultant dilatation and budding of the terminal bronchioles 2 mm in diameter1 photo. BACKGROUND Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported.
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in a 51-year-old man with chronic myelogenous leukemia who underwent bone marrow transplantation. Get prescriptions or refills through a video chat if the doctor feels.
Jennifer hong ba francisca zuazo md hanyuan shi md 1 1 tulane university la new orleans. The tree-in-bud sign has been described in cases of acute aspiration 13. FREE Shipping by Amazon.
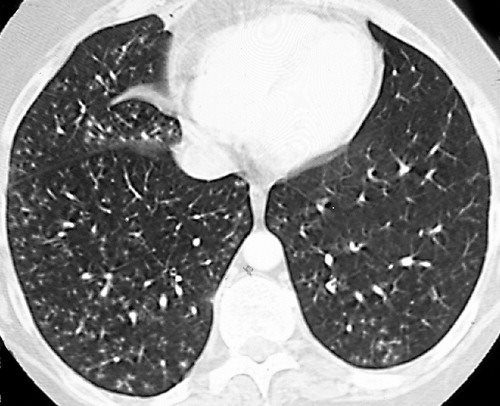
The tree-in-bud pattern might be helpful to choose a suitable therapy in patients with an acid-fast bacilli smear-positive diagnosis of lung disease. 10 coupon applied at checkout Save 10 with coupon. Tree-in-bud refers to a pattern seen on thin-section chest CT in which centrilobular bronchial dilatation and filling by mucus pus or fluid resembles a budding tree Usually somewhat nodular in appearance the tree-in-bud pattern is generally most pronounced in the lung periphery and associated with abnormalities of the larger airways.
This is the classic appearance of the tree in bud pattern seen on chest ct. TIB opacities are most often a manifestation of infections or aspiration and patterns of disease can provide clues to the most likely diagnosis. Get it as soon as Tue Feb 22.
The term comes from a. A Thin-section CT scan of the right lung shows centrilobular ground-glass opacities in addition to nodules and tree-in-bud opacities arrow. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of TIB opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with TIB opacities.
Tree Faces Decor Outdoor Tree Hugger Yard Art Garden Decoration Unique Bird Feeders for Outdoors and Indoors Old Man Tree Art. Lung nodules are usually about 02 inch 5 millimeters to 12 inches 30. TREE-IN-BUD OPACITIES LEADING TO A DIAGNOSIS OF SARCOID.
Intravascular pulmonary tumor embolism often occurs in cancers of the breast liver kidney stomach prostate and ovaries and can lead to the tree-in-bud sign in HRCT 214. 11 TIB opacities represent a central imag- Background. IT IS NOT ALWAYS TUBERCULOSIS.
ODonnell MD The Nehemiah and Naomi Cohen Chair in Pulmonary Disease Research. Ground glass opacity GGO refers to the hazy gray areas that can show up in CT scans or X-rays of the lungs. Other noninfectious conditions that produce bronchiolar impaction and a tree-in-bud.
Tree in bud opacities treatment. Infectious Diseases eg Tuberculosis TB. Hospital Medicine 2020 Virtual Competition.
Mycobacterium avium complex is the most common cause in most series. TIB opacities are also associated with bronchiectasis and small airways obliteration resulting in mosaic air trapping. Colds and coughs stomach symptoms bladder infections rashes and more.
In clinical practice however it can reflect a wide variety of pathogens including bacterial fungal and viral organisms. The tree-in-bud pattern can be an early sign of disease Fig 10 15. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated.
46 out of 5 stars 203. Originally and still often thought to be specific to endobronchial Tb the sign is actually non-specific and is the manifestation of pus. The purpose of this study was to.
In TB the lesions are often present in the apical and posterior segments of the upper lobes and in the superior segments of the lower lobes. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of causes of tib opacities and identify patterns of disease associated with tib opacities. However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated.
1 direct filling of the centrilobular arteries by tumor emboli and 2 fibrocellular intimal hyperplasia due to carcinomatous. What does tree in bud mean. Mycobacteriumabscess lung disease acid-fast bacilli smear positive lung disease chest CT performance.
The tree-in-bud sign is a nonspecific imaging finding that implies impaction within bronchioles the smallest airway passages in the lung. 2 However the classic cause of tree-in-bud is Mycobacterium tuberculosis especially when it is active and contagious and associated with cavitary lesions. The latter etiology is often overlooked but is important to consider in patients with a cancer history to avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Infection is most often responsible for consolidations and nodules with bubble-like lucencies. The tree-in-bud pattern occurs commonly in patients with endobronchial spread of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is highly suggestive of active tuberculosis 2 3High-resolution CT usually reveals small 24-mm centrilobular nodules and branching linear opacities of similar caliber originating from a single stalk Figs 2 3 4. 2 There may be a tree-in-bud sign reflecting the endobronchial spread of infection.
The tree-in-bud pattern is classically associated with endobronchial spread of tuberculosis or atypical mycobacterial infection. A tree-in-bud pattern of centrilobular nodules from metastatic disease occurs by two mechanisms. Video chat with a US.
Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. Tree-in-bud pattern seen on high-resolution CT HRCT indicates dilatation of bronchioles and their filling by mucus pus or fluid. These gray areas indicate increased density inside the lungs.
In radiology the tree-in-bud sign is a finding on a CT scan that indicates some degree of airway obstruction.

Chest Ct With Multifocal Tree In Bud Opacities Diffuse Bronchiectasis Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Tree In Bud Semantic Scholar

Bronchial Cyst Azygoesophgeal Recess Typical Location Cysts Bronchial Radiology
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Bronchiolitis Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org Radiology Bud Pattern
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Tree In Bud Sign An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

References In Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Chest

Tree In Bud Opacities With False Positive Gaffky Score And Diffuse Aspiration Bronchiolitis Mogi 2020 Journal Of General And Family Medicine Wiley Online Library